
wants to build large scale data processing systems.
This was done as a term project for the partial fulfillment of course ‘Compiler Construction’
The project involves the construction of a simple compiler for a reduced C-like high-level dummy language called ERPLAG. It generates an intermediate NASM-assembly code for the given source code, which can then be converted to the machine dependent binary executable.
The project involves the various steps of evaluation from performing lexical, syntactic and semantic checks to setting up relevant data structures to hold information and performing code optimizations.
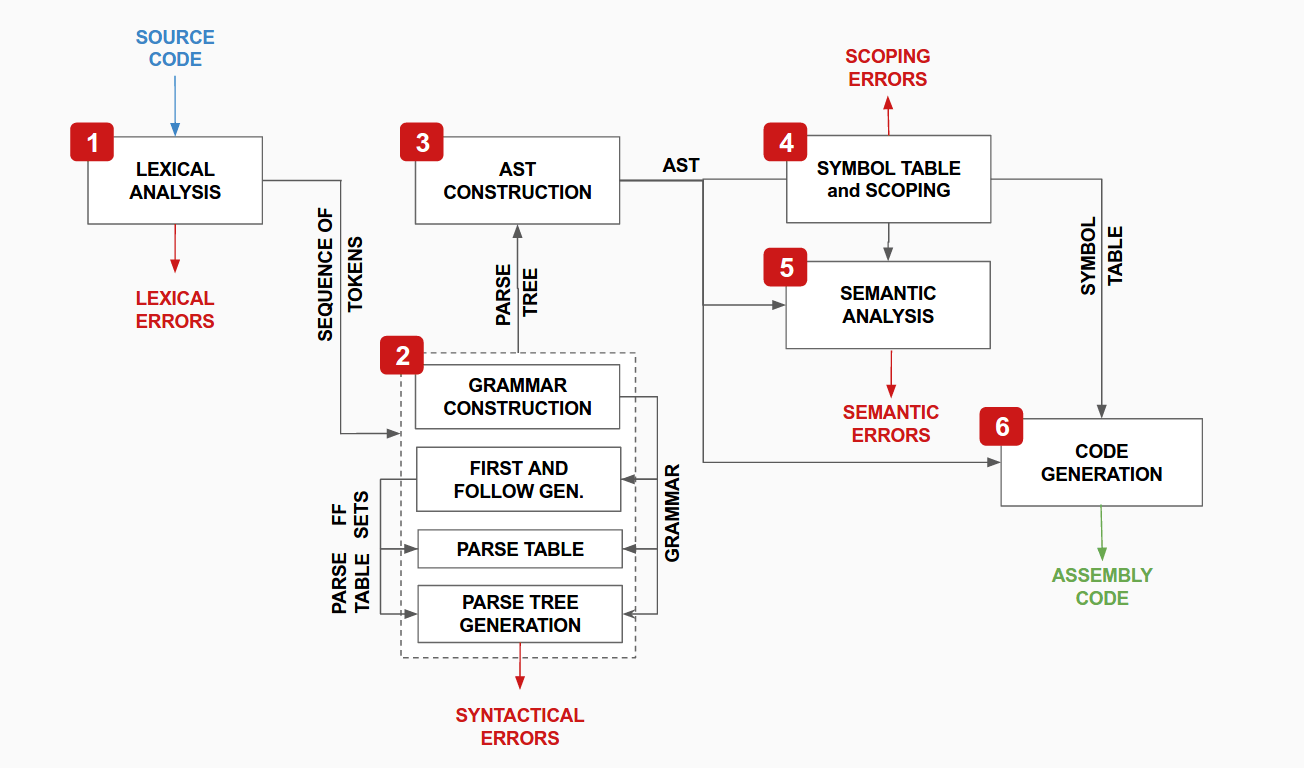
# Modules
- Lexer (lexer.c) : the module reads the source code in HLL as a stream of charaters and converts sequence of characters to meaningful tokens that represents the various keywords, operators, variable and constants in the source code. This module also handles the lexical errors that arise out of improper sequence of characters in the source file.The tokens are passed to the parser and contains information about the line of occurrence, name of the token, token id, value etc.
- Parser (parser.c) : parser takes in the sequence of tokens and verifies the syntactical correctness of the source code by constructing the parse tree in the top-down approach. It reports all the syntactic errors in the code that arises out of improper construct of tokens and also has error recovery mechanism to parse the remaining code, in case of an error. The module starts by setting up the rules of the LL(1) grammar in proper structures and creating the parse table. It then uses the parse table and sequence of tokens to create the parse tree which is further used to verify the semantic correctness of the code and generate intermediate code.
-
AST Construction (ast.c) : this module performs optimization on the constructed parse tree by performing the following operations on it :
- Deleting all the irrelevant tokens that do not give useful information
- Changing the structure of
to infix notation (for proper checking and evaluation) - removing chaining in the tree as a result of unambiguous and LL(1)-compatible grammar.
- removing empty non-terminals, i.e, non-terminals with no children.
The resultant structure has the same node structure as that of the parse tree, but with only relevant data for code generation.
- Symbol Table and Scoping (scope.c) : this module constructs the symbol-table for the corresponding Abstract Syntax Tree. The symbol table has a tree structure that depicts the scoping of the blocks of code. Each node of this tree has a linked list of its locally defined variables. This module reports error related to redundant declaration, no declaration of variables and modules and other scope conflicts, if any.
- Type Checker and Semantic Analyser (semantics.c) : this module performs semantic checks on the AST for verifiying semantic correctness of the source code. It also determines the end-type of the expressions and verifies its correctness.
- Code Generation (codegen.c) : Generates the NASM-assembly code of the source code.
Github
https://github.com/g31pranjal/erplag-compiler
# Compatibility
- gcc (Ubuntu 5.4.0-6ubuntu1~16.04.4) 5.4.0 20160609
- NASM version 2.12.01
# Usage
- use
maketo compile the client and server code for the game. - the driver.c is compiled to the executable binary called
comiler. -
run the executable as :
./compiler <path-to-source> <asm-file>
- Select the desired option from the driver menu to evaluate the source code uptill a specific module.
-
For producing the binary from .asm file :
nasm <asm-file> -f elf64 -o <o-file>gcc <o-file> -o <executable>./<executable>